Healing Starts at the Cellular Level: How Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy is Transforming Recovery in 2025
When Medication Isn’t Enough Anymore
Understanding the Basics: What Are UC-MSCs?
-
Bone cells (osteocytes)
-
Cartilage cells (chondrocytes)
-
Fat cells (adipocytes)
-
Muscle cells (myocytes)
-
Neural-supporting cells (glial cells)
-
Higher cell division rate (they multiply faster)
-
Lower risk of immune rejection
-
No ethical controversy — collected non-invasively after birth
The Cellular-Level Mechanism of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy
Homing: Navigating to the Site of Damage
UC-MSCs have receptors that detect and follow these chemical gradients, allowing them to home in on the affected area with precision.
Paracrine Signaling: Orchestrating the Repair
They release bioactive molecules such as:
Becoming the Cells That Are Needed
Calming the Overactive Response
In conditions like autoimmune diseases or chronic inflammation, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. UC-MSCs secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, while reducing pro-inflammatory molecules like TNF-α.
This:

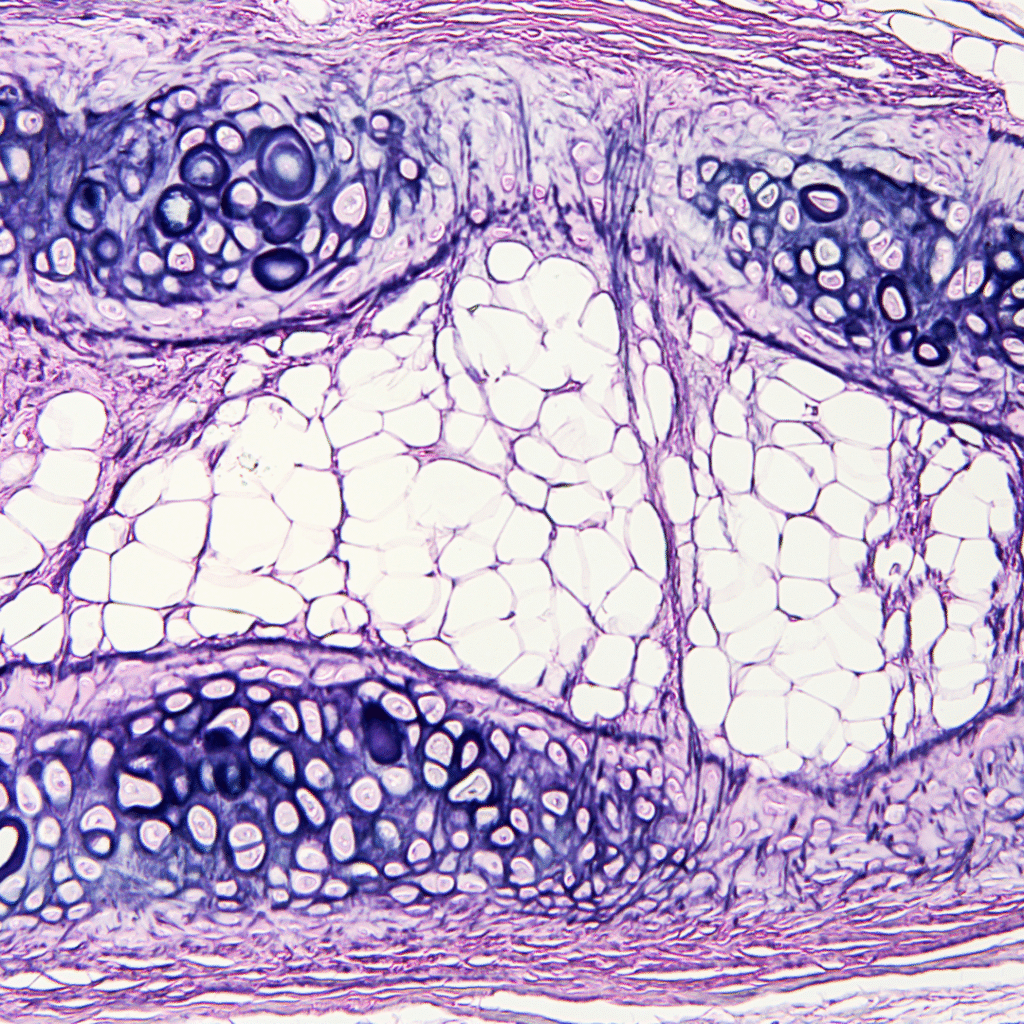
The Science Behind Tissue Repair & Regeneration
Conditions That May Benefit from UC-MSC Therapy
Safety and Ethical Considerations
Why UC-MSCs Are Different from Other Stem Cells
| Feature | UC-MSCs | Adult MSCs | Embryonic Stem Cells |
| Potency | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Ethical Issues | None | None | Controversial |
| Immunogenicity | Low | Moderate | High |
| Collection Method | Non-invasive | Invasive | Requires embryo |
The Future: Combining UC-MSCs with Exosome Therapy
Frequently Asked Questions
Clinical Trials & Research References
- Neurological Disorders
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disorders
- Respiratory Conditions
- Liver Diseases
- Metabolic Disorders
All Rights Reserved 2025